Dental implant is a standardized method of prosthetic rehabilitation of the dentition, which is based on the principle of osseointegration, a biological process of integrating an artificial implant into the maxillary or mandibular bone structures. In clinical practice, dental implants are customized to the patient's needs, and their success depends on treatment planning, the patient's general health, and adherence to postoperative procedures.
What is a dental implant?
A dental implant is an artificial medical device, usually made of titanium or titanium alloys, that is surgically inserted into the jawbone or jawbone to replace the root of a lost tooth. Dental implants are used to provide support for fixed (crowns, bridges) or mobile (dentures) prosthetic restorations, their purpose being to rehabilitate the patient's masticatory, aesthetic and phonetic functions. The procedure is indicated in cases of partial or total edentacy (lack of teeth).
Dental implant - Components
The dental implant is composed of three parts, each with a specific role in the functional and aesthetic rehabilitation of the dentition. The components of a dental implant are:
- the actual implant (the part that inserts into the bone and plays the role of the artificial root);
- the prosthetic abutment (intermediate component that connects the implant and the dental crown);
- the crown/dental work (the visible and aesthetic part of the dental implant, which replaces the natural tooth).
When is a dental implant recommended?
The dental implant is an effective and durable solution for the restoration of lost or damaged teeth, being recommended in several clinical situations. The main indications for dental implants include:
- when one or more teeth are missing;
- if the teeth are cracked or broken;
- in case of dental fractures;
- in case of facial trauma.
Dental implant - Advantages
Dental implants offer multiple advantages compared to other methods of oral rehabilitation, both from an aesthetic and functional point of view. The main advantages include:
- regaining a beautiful smile;
- restoration of functions affected by tooth loss (masticatory and speech function);
- easy hygiene, as in the case of natural teeth;
- long life span;
- prevention of tooth migration;
- high stability.
Types of dental implant at DentArbre
At the Dentarbre clinic, patients have access to different types of dental implants, each designed to meet specific needs and provide optimal long-term results. Among the most popular types of implants available are:
INNO Dental implant
The INNO dental implant stands out for its surface treated to stimulate bone regeneration and for its excellent primary stability, being ideal for patients with low bone density. INNO implants are frequently used in dental clinics due to their versatility and high clinical success rates.
Megagen AnyRidge dental implant
Megagen AnyRidge is a dental implant system acclaimed for its versatility and adaptability to a wide range of clinical conditions. Its design ensures high primary stability, even in low-density bone, and is also suitable for difficult cases.
Dental implant - Stages of the intervention
The procedure of inserting a dental implant is a complex process, involving multiple clinical stages, guided by strict protocols and adapted to the individual needs of each patient, depending on the condition of the alveolar bone, medical history and anatomical parameters.
Consultation
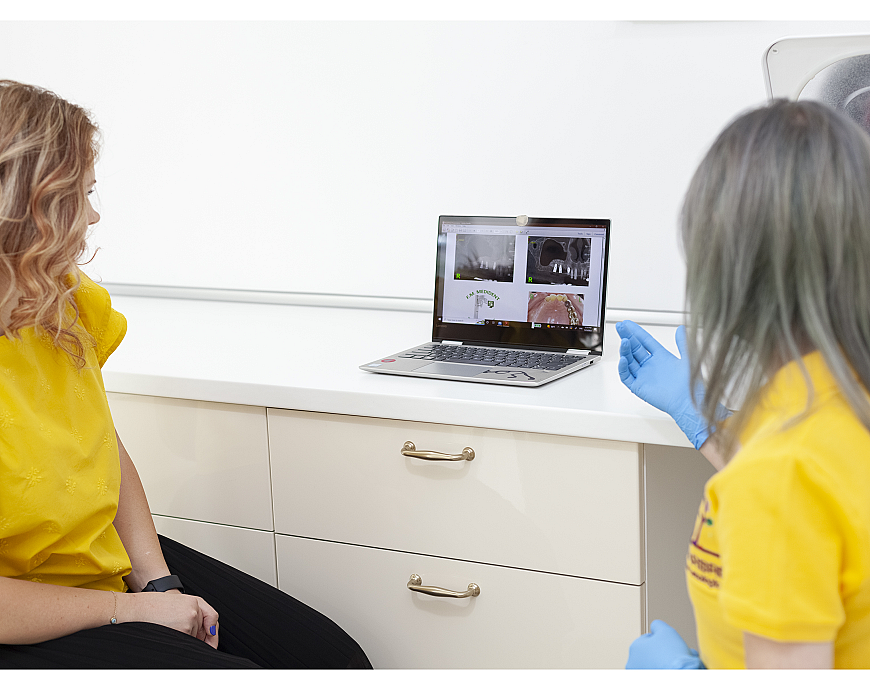
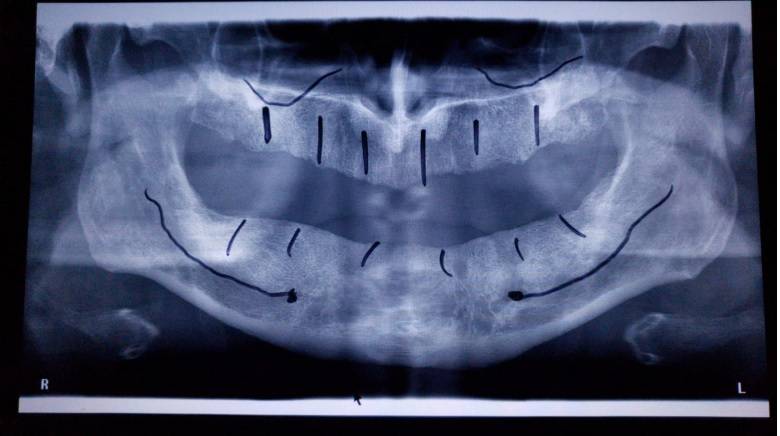
The initial consultation involves clinical and imaging assessment of the patient. The examination of the oral cavity, the dento-periodontal status and the bone architecture is carried out with the help of panoramic radiographs and computed tomography (CT), to determine whether the patient has sufficient bone volume and favorable conditions for osseointegration.
Interpretation of analyzes and results
Laboratory analyzes are necessary to assess the general health of the patient and to exclude relative or absolute contraindications. Patients with systemic conditions such as osteoporosis treated with bisphosphonates or uncontrolled diabetes require special precautions. Based on the results of the analyzes and radiological images, it is decided whether bone augmentation or other preoperative interventions are necessary.
Surgical intervention
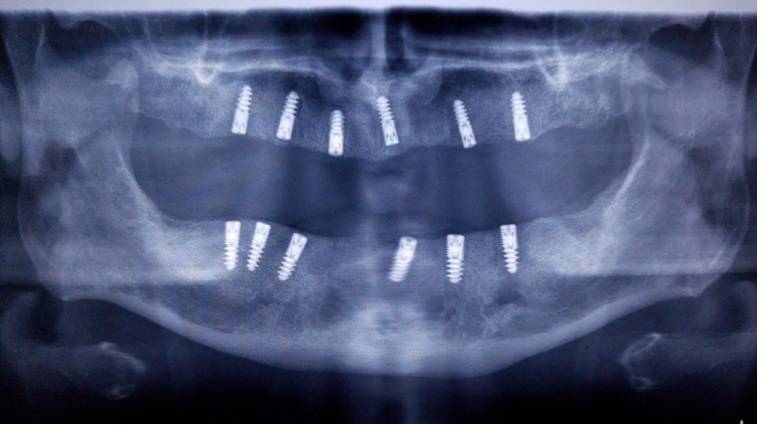
The surgical insertion of the dental implant is performed under local anesthesia and involves the exposure of the alveolar bone through a gingival incision. Depending on bone density and bone morphology, progressively sized burs are used to create a pilot tunnel suitable for implant insertion. The implant, usually made of medical grade titanium (biocompatible) is inserted with controlled torque to ensure primary stability, a critical factor for successful osseointegration. In the case of the presence of insufficient bone volume, bone augmentation or sinus lift techniques can be associated, depending on the location. After inserting the implant, sutures are applied to close the surgical wound.
Sutures removal
The applied sutures are removed approximately 7-10 days postoperatively, depending on the type of sutures and the healing speed of the gum tissue. The doctor will assess the degree of integration and comfort of the patient, providing additional recommendations related to oral hygiene and management of pain or inflammation.
Attaching the healing abutment
After a period of 3 to 6 months of osseointegration (depending on bone density and insertion area), a small incision is made to expose the implant and attach the healing abutment.
Preparation of the dental crown
After the gingival tissues have been correctly modeled, the prosthetic stage takes place. Accurate impressions of the implant position and dental arches are made using either traditional methods or digital techniques. Based on these impressions, the definitive crown is made, which is fixed either by cementation or by direct screwing to the implant.
Dental implant - How does the actual procedure takes place?
The insertion of a dental implant follows a series of sequential steps, which prepare the affected area for implantation and ensure its optimal integration. Steps to follow:
- carrying out the necessary dental extractions, with maximum preservation of the alveolar bone;
- cleaning the area of dental infections;
- restoration of the affected bone;
- preparing the area for inserting the dental implant.
Dental implant - How long does the treatment take?
The duration of the treatment depends on the complexity of each case, the condition of the bone and gum tissues, as well as the need for additional procedures. Implant insertion surgery takes, on average, between 1 and 3 hours, depending on the number of implants inserted and the surgical techniques used (for example, bone augmentation or sinus lift).
24 hours postoperatively, the patient can benefit from the installation of a fixed temporary prosthetic work, which has the role of restoring functionality and immediate aesthetics. The provisional prosthesis is worn during the osseointegration phase, which varies between 3 and 6 months, during which the implant integrates into the maxillary or mandibular bone. After osseointegration, the definitive prosthetic rehabilitation is carried out, by mounting the definitive fixed work, which can be a unitary crown, a dental bridge or a fixed prosthesis on implants, depending on the treatment plan.
What is the cost of a dental implant?
The price of a dental implant can vary significantly depending on the type of implant, the materials used for prosthetic rehabilitation and the complexity of the intervention. Detailed prices for each type of implant, prosthetic abutment and dental crown are available here. Prices do not include any additional procedures, such as bone grafts or guided bone regeneration techniques.
Recommendations for recovery after dental implant
To ensure adequate healing and prevent complications, it is necessary to observe some simple hygienic and dietary measures postoperatively. Among other things, it is recommended:
- avoiding food consumption in the first 2-3 hours after the intervention;
- consumption of soft foods, such as soups or purees, in the first postoperative days;
- brushing your teeth at least twice a day, using a soft brush;
- the use of a non-abrasive toothpaste that does not irritate or damage the peri-implant tissues, especially in the initial healing phase.
Dental implant vs. Dental bridge
Compared to the dental bridge, the dental implant has the major advantage of being an independent restorative solution that does not require the grinding of the surrounding healthy teeth. In addition, the dental implant, under conditions of proper care, has a lifespan that can be significantly longer than that of a dental bridge.
Dental implant vs. Classic prosthesis
Compared to a classic dental prosthesis, dental implants represent a much more stable and functional solution. Traditional prostheses are susceptible to mobility and instability, especially in cases of advanced bone resorption. In comparison, implants provide a fixed anchorage in the bone, which improves masticatory function and speech. Implants also prevent migration of remaining teeth and bone atrophy, common problems in denture wearers.
Dental implant contraindications
Although dental implants can be used successfully in most patients, there are certain situations where, for medical or anatomical reasons, the procedure is not indicated. Contraindications can be absolute or relative, depending on the particular situation of each patient. The procedure is contraindicated:
- in patients with low bone density or severe bone atrophy, as a result of prolonged edentination;
- in patients with autoimmune diseases (patients have an increased risk of failure of osseointegration and the occurrence of peri-implant infections);
- in patients with active periodontal diseases (periodontitis);
- in the case of children and adolescents (the bone growth process is not complete).
Dental implant - Intervention risks
Like any surgical procedure, the insertion of a dental implant involves certain risks. Although the success rate is high, short-term or long-term complications can occur and must be properly managed to prevent treatment failure. Main associated risks:
- soft tissue or bone infections (osteomyelitis) following implant insertion;
- treatment failure, due to inadequate bone volume support;
- nerve damage;
- dental implant rejection.

Dr. Carmen-Nicoleta Radu answers questions:
Prices for Dental Implants
Study cases
See below the clinical cases performed by our team of doctors in each specialty:
- Dental Implants
- Dental Prophylaxis
- Dento-Alveolar Surgery
- Ortodontics. Dental Braces
- Dental Aesthetics
- Dental Prosthesis
- Odontoterapy
- Endodontics
- Pediatric Dentistry
+40787877799 | +40762573398
contact@dentarbre.comȘoseaua Colentina, nr. 16, Bl. A1, Complex Rose Garden, Sector 2, Zona Obor - Colentina - Doamna Ghica