Gingivitis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment for Gingivitis
The health of your gums and teeth reflects your overall health. Healthy gums are firm, dark pink, don’t bleed, and show no signs of pain. If your gums are tender to the touch, inflamed, and dark red, you may have gingivitis. Learn more about the causes and symptoms of gingivitis below, and discover how to prevent and treat it to keep your oral health in tip-top shape.
What is gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common dental condition characterized by superficial inflammation of the gums. Left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. In severe cases, periodontitis can even lead to tooth loss. Unlike periodontitis, gingivitis can be treated and cured if caught early.
Why does gingivitis occur - Causes
Gingivitis is usually caused by bacterial infections. Excessive plaque irritates the gums and causes inflammation and pain. In addition to bacterial infections, gingivitis can also occur due to the following causes:
- Viral or fungal infections;
- Allergic reactions;
- Reactions of the body to foreign bodies (for example, dentures)
Gingivitis is more common in the following categories of patients:
- Pregnant women;
- Patients suffering from hormonal disorders (related to pregnancy, menstrual cycle or contraceptives);
- Patients with poor oral hygiene;
- Patients with dental problems that make brushing difficult;
- Patients with diabetes;
- Patients with a family history of gum disease.
Risk factors for gingivitis
Risk factors that increase the chances of developing gingivitis are:
- Unhealthy habits that influence oral health;
- Smoking;
- Older age;
- Dry mouth syndrome (xerostomia);
- Improper diet;
- Dental work that does not suit the patient;
- Health problems that affect immunity;
- Hereditary factors;
- Certain medications can contribute to the development of gingivitis because they alter normal salivary flow (medications for epilepsy or cancer, calcium channel blockers, contraceptives, etc.).
Types of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is classified according to:
- What the gums look like (clinical appearance) – for example, gingivitis that causes bleeding;
- The cause of gingivitis (etiological aspect) – for example, gingivitis caused by bacterial infections;
- The duration of gingivitis – it can be acute or chronic.
The main types of gingivitis are as follows:
- Plaque-induced gingivitis;
- Infectious gingivitis – which occurs due to infections, allergic reactions, or foreign objects in the mouth.
How gingivitis manifests itself - Symptoms
Symptoms of gingivitis are visible and include:
- Swollen gums;
- Dark red gums;
- Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing;
- Receding gums;
- Bad breath (halitosis);
- Discolored gums;
- Gums that are sensitive and painful to the touch;
- Soft gums.
How to diagnose gingivitis
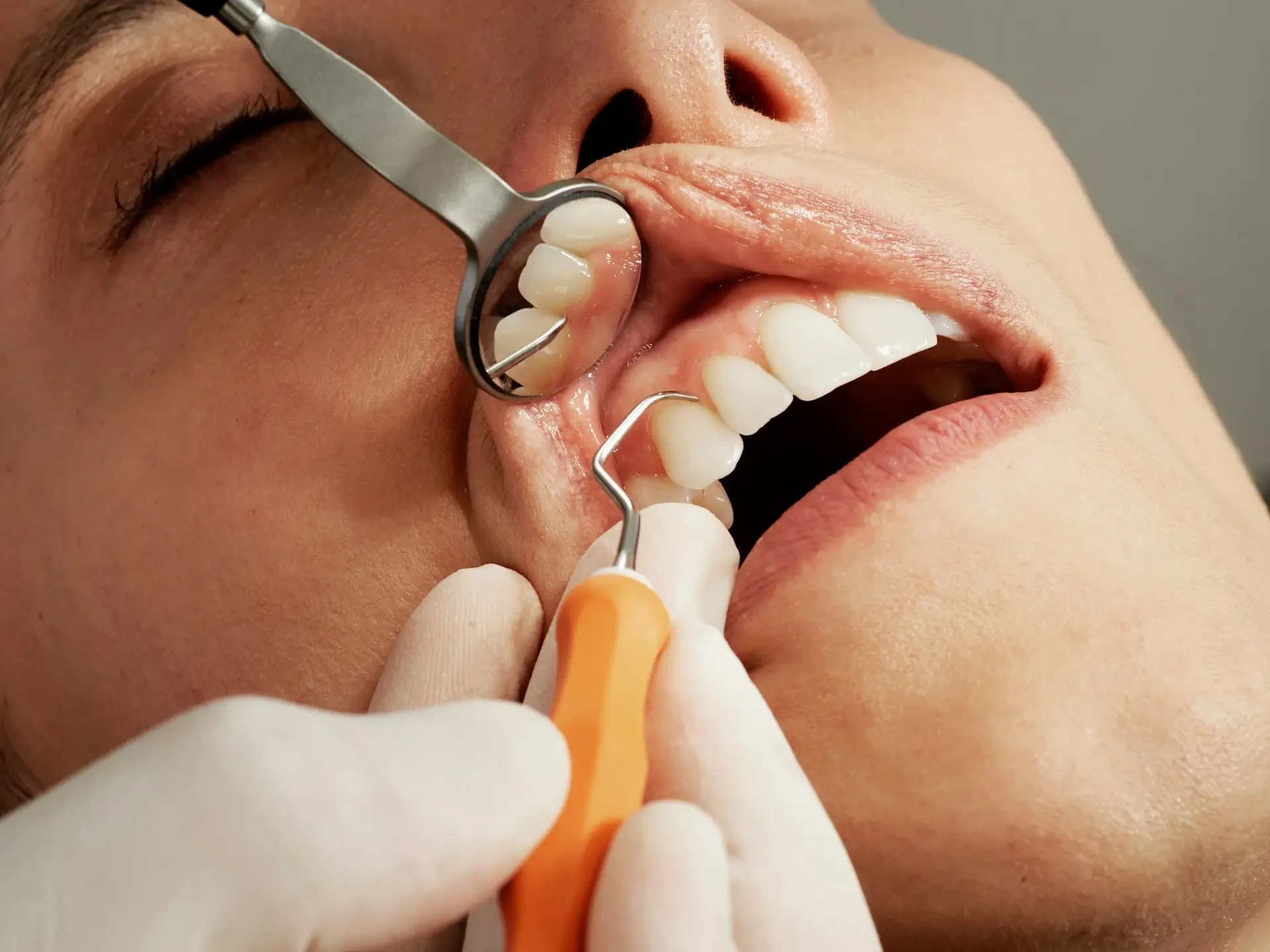
The diagnosis of gingivitis is made during a dental consultation. The dentist checks the appearance of the gums (if they are swollen or bleeding), the depth of the space between the gum and the tooth, the movement, sensitivity and alignment of the teeth. He also examines the jawbone and the presence of bacterial plaque and tartar.
If necessary, additional tests may be recommended to check for the presence of periodontitis. These help to establish a correct diagnosis and adapt the treatment to the specific needs of the patient.
A dental consultation is very important in the prevention and diagnosis of gum problems. If detected in time, gingivitis can be treated and cured, avoiding more serious complications. Schedule a dental consultation right now.
Complications of gingivitis
Untreated gingivitis can lead to serious complications that also affect other structures (jaw bone, periodontal ligaments, teeth, etc.). Complications of gingivitis include:
- Abscess or infections in the gums or jawbone;
- Periodontitis;
- Recurrence of gingivitis;
- Ulceration of the gums.
Proper treatment and compliance with the recommendations of the dentist can prevent these complications. In addition, regular check-ups at the dentist and proper oral hygiene help prevent complications.
Gingivitis in children
The risk of gingivitis in children is influenced by their age and stage of development. Other causes of gingivitis in children can be wearing braces or dental malocclusion.
During the eruption of milk teeth, the gums may become inflamed and bleed easily. The inflammation is temporary and is not a cause for concern. In preschoolers, the risk of gingivitis is quite low, but it increases as the child approaches puberty. Preadolescence and adolescence are the periods with the highest risk of developing the condition, because hormones are in rapid growth, and the gums become more sensitive and susceptible to infection, even with proper dental hygiene.
The symptoms of gingivitis in children do not manifest themselves as intensely as in adults. Children have naturally more prominent gums, and a slight swelling does not necessarily indicate the presence of a serious infection or inflammation. Parents may notice the following symptoms in children:
- Bleeding when brushing;
- Discomfort when chewing;
- Dark gums;
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- Bad breath, even after brushing
To treat gingivitis in children, the first step is to identify the cause of the inflammation. Symptoms will improve once the causative factor is eliminated and appropriate treatment is prescribed. During brushing, soothing gels can be used to reduce discomfort and prevent inflammation.
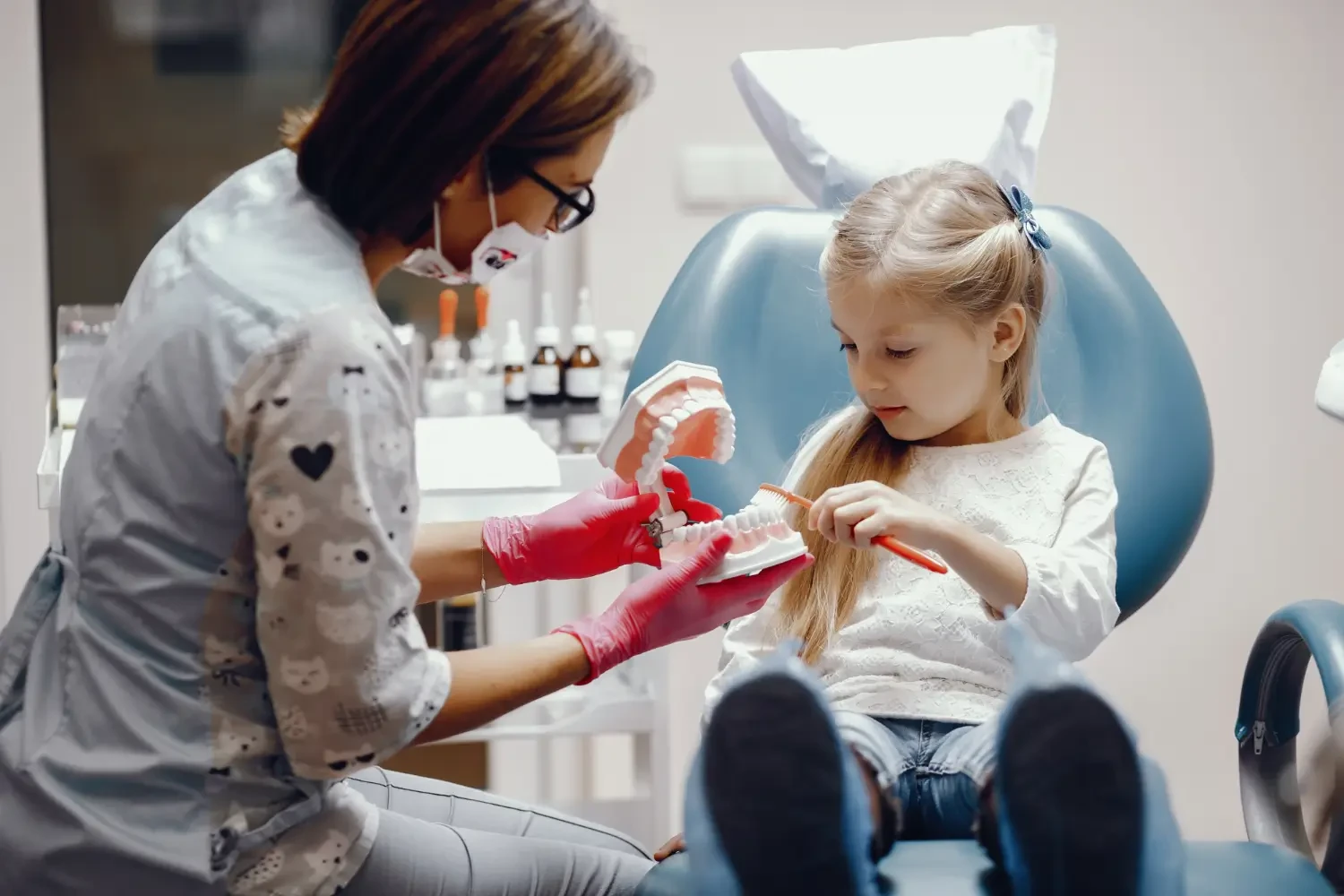

As with cavities, the best way to prevent gum problems in children is proper oral hygiene. Regular tooth brushing, at least twice a day, morning and evening, helps remove plaque. Children's brushing should be supervised by parents until they are 7-8 years old, to ensure that the technique is correct and that the teeth are cleaned adequately. In addition to brushing, dental floss is essential because it helps clean the areas between the teeth where the toothbrush cannot reach. Regular consultation with the pediatric dentist can detect dental problems early.
A daily oral care routine and regular consultation contribute significantly to maintaining the health of the gum tissues and preventing dental diseases in the long term.
Treatment for gingivitis
The treatment for gingivitis aims to control the infection and restore the health of the teeth and gums. The dentist will identify the main factors that cause gum inflammation and prescribe the appropriate treatment for the patient.
Teeth Cleaning
Dental hygiene is the most important for preventing and treating gingivitis. Dental hygiene involves a series of procedures performed by the dentist to remove tartar, plaque, and stains from the teeth.
Scaling is the removal of tartar from the surface of the teeth and around the gums, a major factor in the development of gingivitis. Professional brushing helps to deeply clean the teeth, removing any remnants of plaque and tartar that cannot be removed by daily brushing at home. The airflow method is a gentle technique for the gums, which helps reduce inflammation and discomfort.
Another more modern and less invasive method for removing tartar and bacteria from the teeth is laser treatment.
In more complex cases, the dentist can adjust, repair, or even remove dental work that favors the appearance of gingivitis.
After dental treatment, the doctor will recommend a dental hygiene protocol to be followed at home (special toothpastes for gingivitis, regular brushing, dental floss, antiseptic mouthwash, etc.).
Drug treatment
Only upon the recommendation of a specialist, oral treatment with antibiotics can be prescribed to combat the bacteria causing the infection.
Surgery
In severe cases, especially when there is damage to the supporting tissues of the teeth, surgery may also be recommended.
How to prevent gingivitis
To prevent gingivitis, follow these tips:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day and don't forget to clean your gums, tongue, and palate;
- Change your toothbrush once every three months;
- Use dental floss to clean the spaces between your teeth, where your toothbrush can't reach;
- Use antiseptic mouthwash;
- Quit smoking, as it can worsen gum health and contribute to gingivitis;
- Limit your intake of foods and drinks high in sugar, including alcohol, as they promote the growth of bacteria that cause gingivitis;
- Visit your dentist at least once a year for regular checkups and to prevent more serious dental problems.
Frequently asked questions about gingivitis
Find out how long it takes for gingivitis to heal, what risks are associated with untreated gingivitis, how it can affect pregnancy, and what treatments are most effective for controlling it.
Photo source: Unsplash, Freepik
Bibliography:
· www.healthline.com, https://www.healthline.com/health/gingivitis, accessed 28.02.2024;
· www.medicalnewstoday.com, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/241721, accessed 28.02.2024;
· my.clevelandclinic.org, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10950-gingivitis-and-periodontal-disease-gum-disease, accessed 28.02.2024;
· www.mayoclinic.org, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gingivitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354453, accessed 28.02.2024.

Dr. Nicoleta Taran answers questions:
-thumb_1x.png )